Discover how digital nomads impact local communities with economic boosts, cultural exchange, and challenges like gentrification. Explore Chiang Mai’s case study.
Digital nomadism, a lifestyle where individuals leverage technology to work remotely while traveling, has surged in popularity, reshaping economies and cultures worldwide. With an estimated 63 million digital nomads globally contributing approximately US$787 billion annually, their influence is undeniable. However, their presence sparks debate: do digital nomads bring prosperity and diversity to local communities, or do they exacerbate challenges like gentrification and cultural disconnect? This article delves into the multifaceted impacts of digital nomads, drawing insights from research, particularly a case study on Chiang Mai, Thailand—the world’s “digital nomad capital”—and offers strategies for balancing their benefits and challenges.
The Rise of Digital Nomadism
Digital nomadism represents a paradigm shift in work and lifestyle. Enabled by advancements in technology and the gig economy, professionals—freelancers, consultants, and entrepreneurs—work remotely from diverse locations, from bustling cities to tropical beaches. In the U.S., about 17.3 million workers (11% of the workforce) identify as digital nomads. Globally, nearly 60 countries have introduced digital nomad visas to attract these mobile professionals, recognizing their potential to stimulate local economies.
Chiang Mai, Thailand, exemplifies this trend. Known for its low cost of living, rich cultural heritage, and reliable infrastructure, it has become a hub for digital nomads. Research from the UNSW Business School and other institutions highlights Chiang Mai as a case study to understand the broader implications of this lifestyle on local communities.
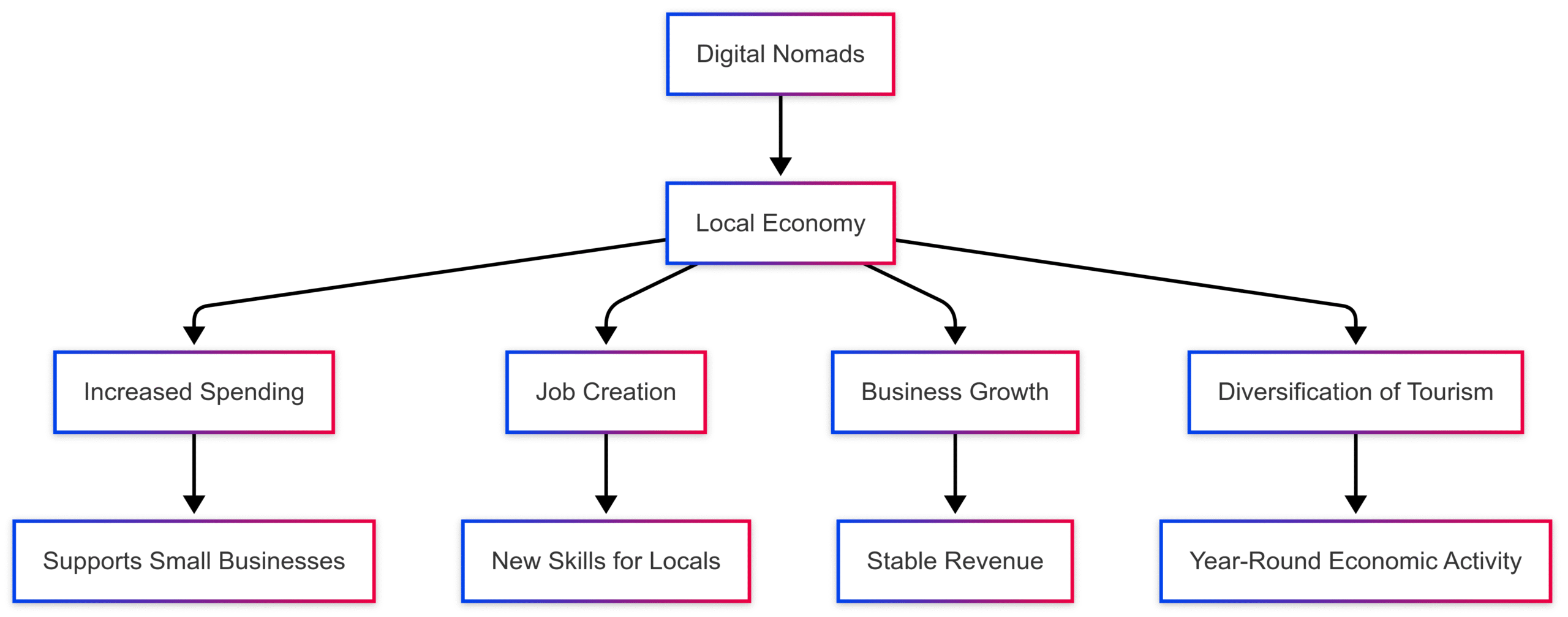
Economic Impacts: A Boon for Local Economies
Digital nomads inject significant capital into local economies, fostering growth in various sectors. Their spending patterns and longer stays compared to traditional tourists create a stable economic boost, particularly in regions like Chiang Mai.
Increased Spending
Digital nomads, often earning incomes from higher-wage countries, spend generously on accommodation, dining, transportation, and entertainment. In Chiang Mai, they frequent local cafes, restaurants, and markets, directly supporting small businesses. For instance, a study estimates that attracting 100,000 digital nomads annually to Greece, with an average stay of six months, could generate revenue equivalent to 2.5 million week-long tourist visits. Similarly, Barbados’ Welcome Stamp program generated US$6 million in visa fees and US$100 million in tourism revenue from just 2,500 applicants in its first ten months.
Job Creation
The influx of digital nomads drives demand for services like co-working spaces, food delivery, and accommodation, creating jobs for locals. In Chiang Mai, the rise of co-working hubs has employed local staff and facilitated workshops, benefiting both nomads and residents. These jobs often require new skills, such as English proficiency or digital literacy, empowering locals with transferable expertise.
Business Growth
Local businesses, from cafes to boutique shops, thrive due to nomad patronage. Unlike seasonal tourists, digital nomads provide consistent revenue, reducing economic volatility. In Chiang Mai, platforms like Airbnb distribute revenue more evenly compared to traditional tourism, supporting a broader range of local entrepreneurs.
Diversification of Tourism
Digital nomads offer a sustainable alternative to seasonal tourism. Their extended stays—often months rather than weeks—stabilize local economies. Chiang Mai’s appeal as a year-round destination has grown, reducing reliance on peak tourist seasons.
| Economic Impact | Description | Example (Chiang Mai) |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Spending | Nomads spend on local goods and services | Boosts revenue for cafes, restaurants, and markets |
| Job Creation | Demand for services creates employment | Co-working spaces hire local staff |
| Business Growth | Consistent patronage supports small businesses | Local shops benefit from year-round nomad spending |
| Tourism Diversification | Long-term stays stabilize economy | Reduces reliance on seasonal tourism |
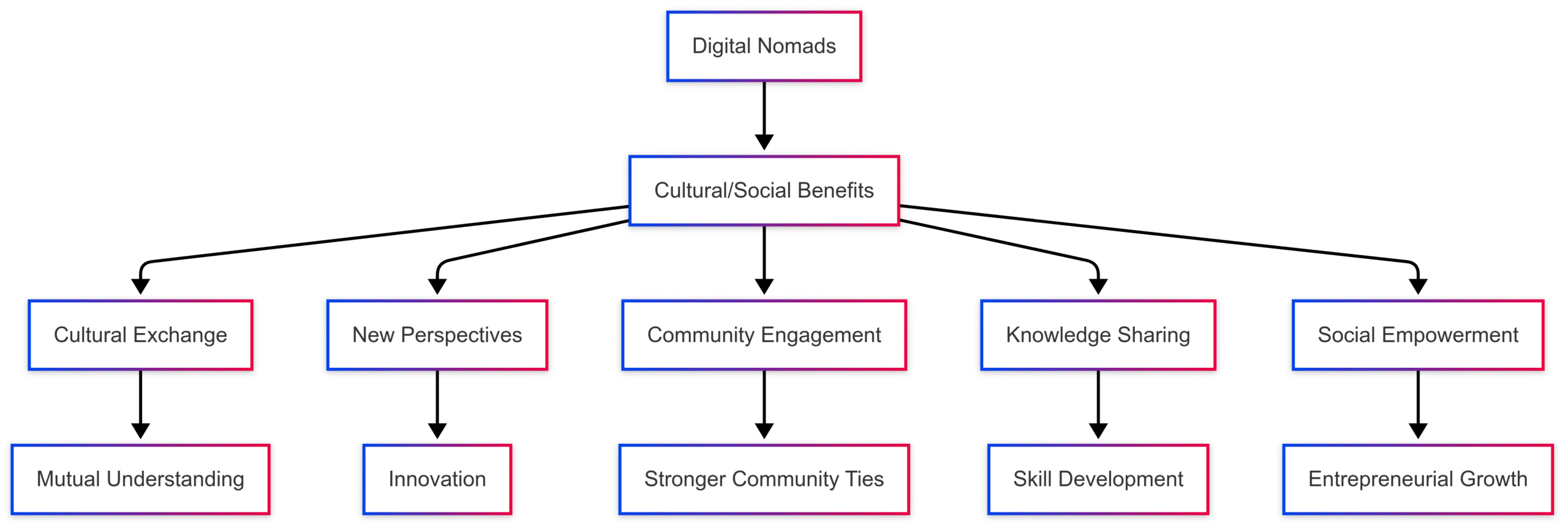
Cultural and Social Benefits: Enriching Communities
Beyond economics, digital nomads foster cultural exchange and community engagement, enriching local societies with diverse perspectives and knowledge.
Cultural Exchange
Nomads bring global perspectives to local communities, engaging with traditions and customs. In Chiang Mai, interactions at co-working spaces and community events facilitate mutual understanding. Locals gain exposure to international cultures, while nomads immerse themselves in Thai traditions, creating a vibrant cultural dialogue.
New Perspectives and Innovation
The diverse backgrounds of digital nomads introduce fresh ideas, sparking innovation. In Chiang Mai, nomads have inspired locals to pursue remote work or entrepreneurial ventures, diversifying the local economy. Workshops and collaborations in co-working spaces often lead to creative projects, benefiting both parties.
Community Engagement
Digital nomads frequently participate in local events, volunteer, or collaborate on community projects. In Chiang Mai, they organize events like tech meetups, fostering connections with locals. Such engagement strengthens community ties and promotes inclusivity.
Knowledge Sharing
Nomads share skills in IT, marketing, or entrepreneurship, empowering locals. In Chiang Mai, training sessions in co-working hubs have equipped residents with digital skills, opening new career paths. This knowledge transfer aligns with sustainable development goals, enhancing local capabilities.
Social Empowerment
By demonstrating remote work’s viability, digital nomads inspire locals to explore similar opportunities. In Chiang Mai, this has led to increased entrepreneurial activity, with locals launching startups or seeking remote contracts, boosting economic independence.
| Cultural/Social Benefit | Description | Example (Chiang Mai) |
|---|---|---|
| Cultural Exchange | Interaction fosters mutual understanding | Nomads attend local festivals |
| New Perspectives | Diverse ideas spark innovation | Locals inspired to start businesses |
| Community Engagement | Participation in local events | Nomads organize tech meetups |
| Knowledge Sharing | Skill transfer to locals | IT workshops in co-working spaces |
| Social Empowerment | Inspires entrepreneurial mindset | Locals pursue remote work |
Challenges of Digital Nomadism
Despite their benefits, digital nomads pose challenges, including economic disparities, social isolation, and environmental concerns, which require careful management.
Economic and Cultural Disparities
The influx of nomads can drive up living costs, particularly housing, leading to gentrification. In Chiang Mai, rising rents have displaced some locals, creating socioeconomic tensions. Nomads’ higher incomes can exacerbate disparities, making local goods and services less affordable for residents.
Social Isolation
The transient nature of digital nomadism can hinder deep community connections. Nomads may prioritize work over engagement, leading to superficial interactions. In Chiang Mai, language barriers and cultural differences sometimes limit meaningful exchanges, isolating both nomads and locals.
Environmental Impact
Frequent travel, especially air travel, contributes to carbon emissions. In Chiang Mai, nomads’ reliance on short-term rentals and transportation strains local resources. Sustainable practices, like eco-friendly accommodations or public transport, are critical to mitigate this impact.
Case Study: Chiang Mai, the Digital Nomad Capital
Chiang Mai’s transformation into a digital nomad hub illustrates both the opportunities and challenges of this lifestyle. Its low cost of living, reliable internet, and vibrant culture attract thousands of nomads annually. Research by UNSW Business School and others reveals key insights:
- Economic Growth: Nomads have spurred the development of co-working spaces, creating jobs and training opportunities for locals. Their spending supports a wide range of businesses, from cafes to tour operators.
- Cultural Exchange: Events like tech meetups and cultural festivals foster interaction, enriching both nomads and residents.
- Challenges: Gentrification and rising costs have strained local communities, highlighting the need for balanced policies.
Professor Daniel Schlagwein notes that Chiang Mai could become the “Singapore of remote work,” leveraging its appeal to drive innovation and entrepreneurship. However, cultural sensitivity and sustainable practices are essential to maintain harmony.
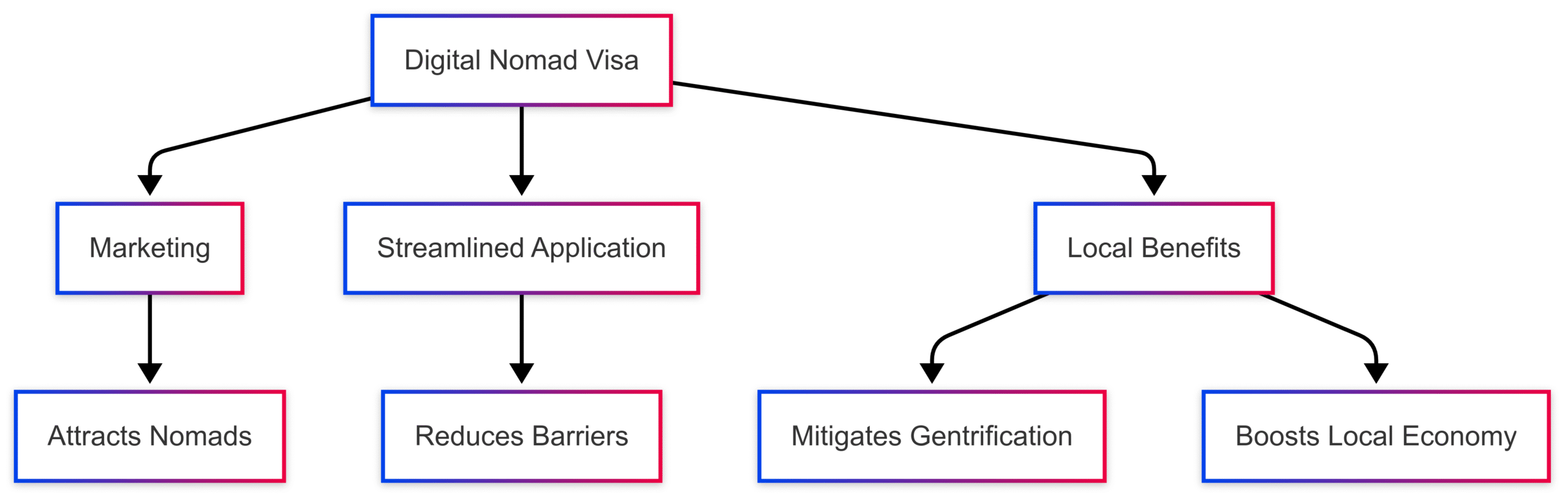
Digital Nomad Visas: Opportunities and Considerations
Nearly 60 countries offer digital nomad visas, recognizing their economic potential. These visas provide temporary residency for remote workers, often with income requirements to ensure economic contributions. Examples include:
- Barbados Welcome Stamp: Generated US$6 million in fees and US$100 million in tourism revenue.
- Estonia Digital Nomad Visa: Integrates with the e-Residency program, fostering startup engagement.
- Malaysia Nomad Pass: Targets digital professionals, connecting them with local businesses.
| Country | Visa Name | Key Features | Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barbados | Welcome Stamp | High-income requirement, 1-year stay | US$100M tourism revenue |
| Estonia | Digital Nomad Visa | Links to e-Residency, startup focus | Boosts tech ecosystem |
| Malaysia | Nomad Pass | Targets digital professionals | Enhances local business connections |
A successful visa program requires:
- Effective Marketing: Promote lifestyle benefits like culture, infrastructure, or adventure.
- Streamlined Applications: Online processes reduce bureaucratic hurdles.
- Local Benefits: Policies should mitigate gentrification and ensure economic gains for residents, such as incentivizing off-season stays or rural housing.
Ethical Digital Nomadism: Balancing Freedom and Responsibility
To maximize benefits and minimize harm, digital nomads must adopt ethical practices. A checklist for responsible nomadism includes:
- Research Local Culture: Learn customs, language basics, and sensitive topics.
- Support Local Businesses: Prioritize local markets and eco-conscious services.
- Engage in Cultural Exchange: Attend events and share skills with locals.
- Minimize Environmental Impact: Use public transport and eco-friendly accommodations.
- Mitigate Economic Disparities: Budget responsibly to avoid inflating costs.
- Ensure Legal Compliance: Adhere to visa and tax regulations.
- Evaluate Community Impact: Volunteer and support local initiatives.
Policy Recommendations for Local Leaders
Governments and communities can optimize the digital nomad trend by:
- Developing Infrastructure: Ensure reliable internet and affordable accommodations.
- Fostering Collaboration: Organize events to facilitate nomad-local interactions.
- Implementing Sustainable Policies: Mitigate gentrification through housing regulations and off-season incentives.
- Promoting Cultural Sensitivity: Educate nomads on local customs to enhance integration.
Conclusion: A Net Positive with Responsible Management
Digital nomads offer substantial benefits to local communities, from economic growth to cultural enrichment, as seen in Chiang Mai’s evolution into a global hub. Their spending, job creation, and knowledge sharing drive sustainable development, while their diverse perspectives foster innovation. However, challenges like gentrification, social isolation, and environmental impact require proactive solutions.
By adopting ethical practices and implementing well-designed visa programs, digital nomads and local communities can create a symbiotic relationship. Governments should prioritize policies that balance economic gains with social and environmental sustainability, ensuring digital nomadism remains a force for good. As the world embraces this evolving work landscape, collaboration between nomads, locals, and policymakers will shape a future where global mobility enriches all.
Please share this Digital nomads: a benefit or burden for local communities? with your friends and do a comment below about your feedback.
We will meet you on next article.
Until you can read, 8 Remote Places with Reliable Internet for Digital Nomads
